Ebola Communication Preparedness Implementation Kit
 Now also available in French, this toolkit developed by CCP provides national and local stakeholders, as well as program managers, with key considerations and a roadmap for instituting and implementing critical, relevant, practical and timely communication for responding to the threat of an Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) outbreak. The I-Kit guides countries in social and behavior change communication (SBCC) and risk communication activity planning, including communication plan development for every stage of an Ebola response. For any country facing a major health crisis, national preparedness plans need to include and support communication efforts. Integration of communication into the preparedness agenda from the outset ensures that preparedness communication is harmonized, relevant, timely, financially supported and aligned among all of the preparedness technical teams. Robust national communication preparedness plans maximize the effectiveness of Ebola communication and equip communication trainers and experts with a common set of tools and modules.
Now also available in French, this toolkit developed by CCP provides national and local stakeholders, as well as program managers, with key considerations and a roadmap for instituting and implementing critical, relevant, practical and timely communication for responding to the threat of an Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) outbreak. The I-Kit guides countries in social and behavior change communication (SBCC) and risk communication activity planning, including communication plan development for every stage of an Ebola response. For any country facing a major health crisis, national preparedness plans need to include and support communication efforts. Integration of communication into the preparedness agenda from the outset ensures that preparedness communication is harmonized, relevant, timely, financially supported and aligned among all of the preparedness technical teams. Robust national communication preparedness plans maximize the effectiveness of Ebola communication and equip communication trainers and experts with a common set of tools and modules.
Sources:


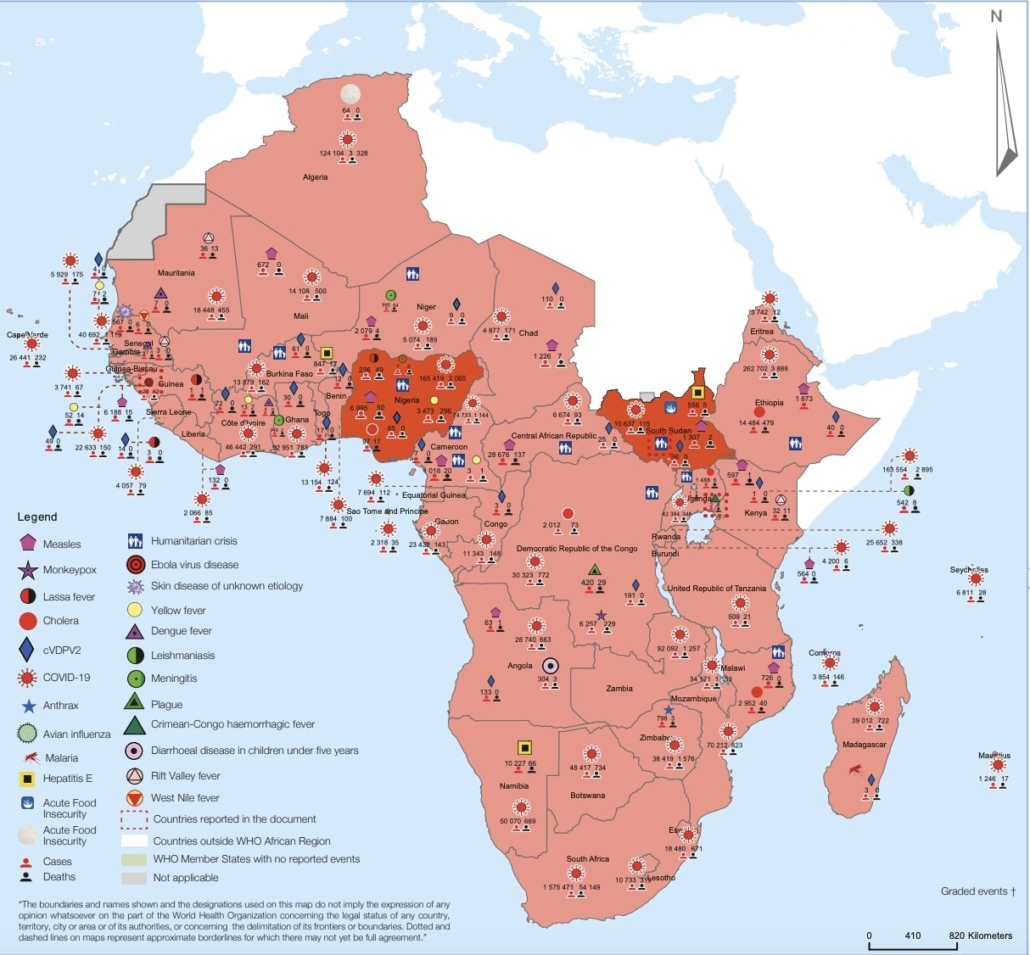 This Weekly Bulletin focuses on public health emergencies occurring in the WHO African Region. The WHO Health Emergencies Programme is currently monitoring 129 events in the region. Weekly articles cover a range of diseases and currently include, amongst others: COVID-19 across the WHO African region and Ebola virus disease in Guinea.
This Weekly Bulletin focuses on public health emergencies occurring in the WHO African Region. The WHO Health Emergencies Programme is currently monitoring 129 events in the region. Weekly articles cover a range of diseases and currently include, amongst others: COVID-19 across the WHO African region and Ebola virus disease in Guinea.
 This poster illustrates the correct ways to protect against Ebola. For example: do not touch people with signs of Ebola or who have died of Ebola, but instead always wash your hands with soap and water.
This poster illustrates the correct ways to protect against Ebola. For example: do not touch people with signs of Ebola or who have died of Ebola, but instead always wash your hands with soap and water.
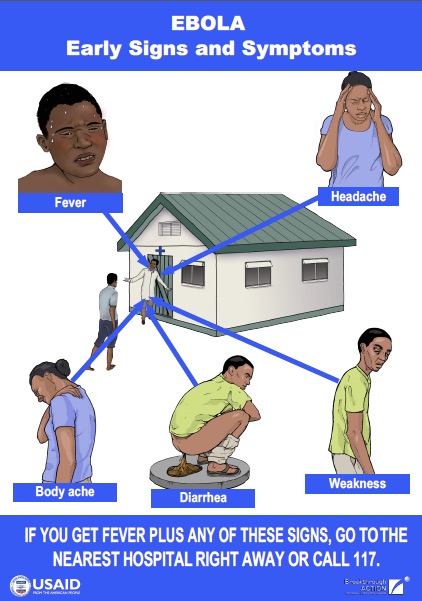 This poster illustrates the early signs and symptoms of Ebola. Early symptoms include: fever, headache, body ache, diarrhea and weakness.
This poster illustrates the early signs and symptoms of Ebola. Early symptoms include: fever, headache, body ache, diarrhea and weakness.
 This illustrated brochure provides facts on EVD, how Ebola is spread, prevention methods and signs and symptoms.
This illustrated brochure provides facts on EVD, how Ebola is spread, prevention methods and signs and symptoms.
 This resource provides lessons from previous Ebola outbreaks in the DRC on adapting to the language needs of communities and centers language as a key trust builder between communities and public health experts.
This resource provides lessons from previous Ebola outbreaks in the DRC on adapting to the language needs of communities and centers language as a key trust builder between communities and public health experts.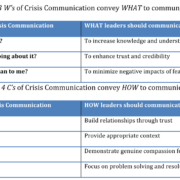
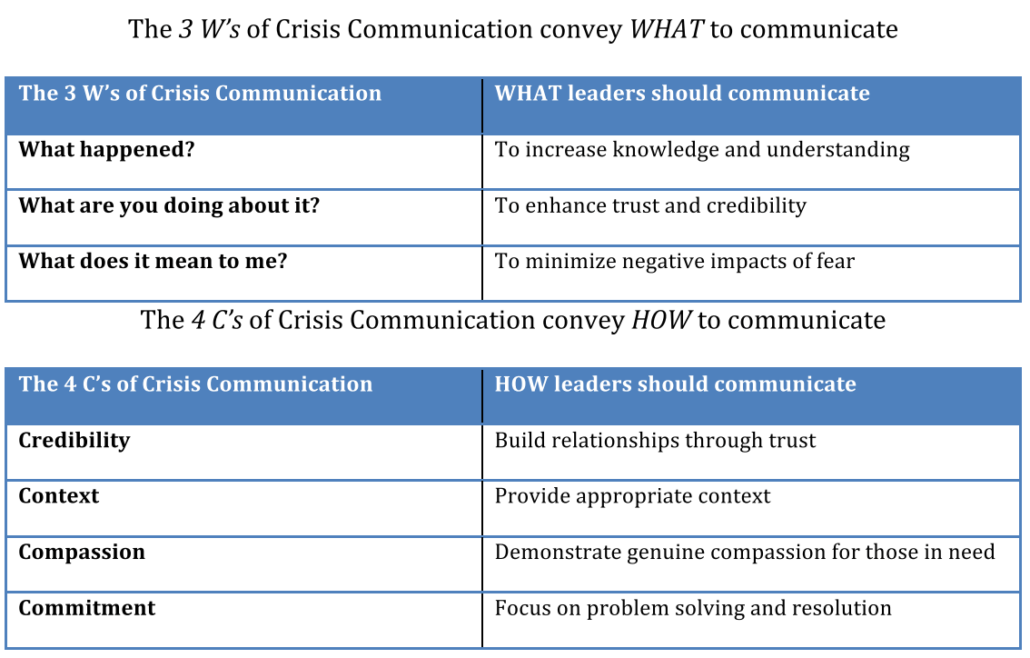 This article (published in Military Medicine (2020) provides tips for leaders on “what to communicate and how to communicate” during a crisis, using lessons learned from the Ebola outbreak as well as lessons now emerging from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. This perspective offers practical guidelines for leaders identified here as the 3 W’s and 4C’s of crisis communication.
This article (published in Military Medicine (2020) provides tips for leaders on “what to communicate and how to communicate” during a crisis, using lessons learned from the Ebola outbreak as well as lessons now emerging from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. This perspective offers practical guidelines for leaders identified here as the 3 W’s and 4C’s of crisis communication.
 This journal article examines structured community engagement initiatives and real-time monitoring of community engagement activities during large-scale epidemics. Researches analysed the Community Led Ebola Action (CLEA) approach implemented through the Social Mobilization Action Consortium (SMAC) during the 2014–2016 Ebola epidemic in Sierra Leone, demonstrating how large-scale, coordinated community engagement interventions can be achieved and monitored in real-time during future Ebola epidemics and other similar epidemics.
This journal article examines structured community engagement initiatives and real-time monitoring of community engagement activities during large-scale epidemics. Researches analysed the Community Led Ebola Action (CLEA) approach implemented through the Social Mobilization Action Consortium (SMAC) during the 2014–2016 Ebola epidemic in Sierra Leone, demonstrating how large-scale, coordinated community engagement interventions can be achieved and monitored in real-time during future Ebola epidemics and other similar epidemics.
 This WHO guide for emergency risk communication (ERC) policy and practice provides overarching, evidence-based guidance on how risk communication should be practiced in an emergency. The recommendations also guide countries on building capacity for communicating risk during health emergencies.
This WHO guide for emergency risk communication (ERC) policy and practice provides overarching, evidence-based guidance on how risk communication should be practiced in an emergency. The recommendations also guide countries on building capacity for communicating risk during health emergencies.
 2021- Developed by the Government of Sierra Leone, this resource features facts about Ebola, prevention, signs and symptoms, treatment and how to distinguish between COVID-19 and Ebola Virus Disease.
2021- Developed by the Government of Sierra Leone, this resource features facts about Ebola, prevention, signs and symptoms, treatment and how to distinguish between COVID-19 and Ebola Virus Disease.