Reported Cases & Percentage of Households with Mobile Phones
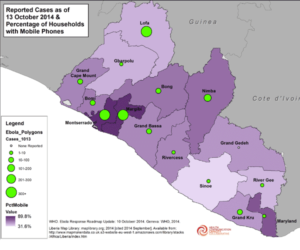 Reported Ebola Cases & Percentage of Households with Mobile Phones, as of October 13, 2014 (Full Size JPG)
Reported Ebola Cases & Percentage of Households with Mobile Phones, as of October 13, 2014 (Full Size JPG)
 Reported Ebola Cases & Percentage of Households with Mobile Phones, as of October 13, 2014 (Full Size JPG)
Reported Ebola Cases & Percentage of Households with Mobile Phones, as of October 13, 2014 (Full Size JPG)
 Report of the WHO Expert Consultation on Outbreak Communications held in Singapore, 21–23 September, 2004.
Report of the WHO Expert Consultation on Outbreak Communications held in Singapore, 21–23 September, 2004.
Outbreak Communication: Best practices for communicating with the public during an outbreak.
 The WHO Regional Office for Africa has worked closely with public health leaders and subject-matter experts in the region and partner organizations to draw up and design this framework to serve as a concise and easy-to-use technical and managerial guide for senior level decision-makers and members of national emergency management committees (EMCs) and rapid response teams (RRTs) in member states.
The WHO Regional Office for Africa has worked closely with public health leaders and subject-matter experts in the region and partner organizations to draw up and design this framework to serve as a concise and easy-to-use technical and managerial guide for senior level decision-makers and members of national emergency management committees (EMCs) and rapid response teams (RRTs) in member states.
 This study was carried out to better understand the local beliefs and practices likely to enhance or hinder efforts to respond to the Ebola Virus Disease outbreak in Liberia.
This study was carried out to better understand the local beliefs and practices likely to enhance or hinder efforts to respond to the Ebola Virus Disease outbreak in Liberia.
Medical Anthropology Study of the Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Outbreak in Liberia/West Africa

This guide will be useful for designing more effective outbreak response measures. It can be scaled up or down, depending on the situation. It can be applied at sub-national and national levels and was designed for developmental communication and health promotion personnel working in multidisciplinary teams to investigate and respond to disease outbreaks.
This poster lists and illustrates five ways to keep Ebola from spreading:
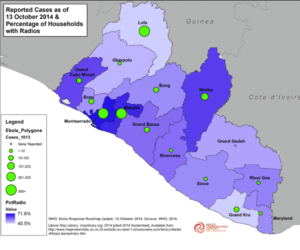 Reported Ebola Cases & Percentage of Households with Radios, as of October 13, 2014 (Full Size JPG)
Reported Ebola Cases & Percentage of Households with Radios, as of October 13, 2014 (Full Size JPG)
 World Health Organization report presenting a draft verbal autopsy instrument based on best judgement and previous experience in a variety of settings including outbreaks and research. It is part of a wider effort by the Global Outbreak Alert and Response Network (GOARN) to develop tools for testing in advance of outbreak situations. The report also contains information on how to carry out a validation study, which compares the results of a verbal autopsy questionnaire with the results of a “gold standard” – such as laboratory test or clinical diagnosis. To date, there is no standard, verbal autopsy instrument for use during outbreaks of Ebola virus haemorrhagic fever (EHF).
World Health Organization report presenting a draft verbal autopsy instrument based on best judgement and previous experience in a variety of settings including outbreaks and research. It is part of a wider effort by the Global Outbreak Alert and Response Network (GOARN) to develop tools for testing in advance of outbreak situations. The report also contains information on how to carry out a validation study, which compares the results of a verbal autopsy questionnaire with the results of a “gold standard” – such as laboratory test or clinical diagnosis. To date, there is no standard, verbal autopsy instrument for use during outbreaks of Ebola virus haemorrhagic fever (EHF).

The Ebola Communication Network was originally developed by the Health Communication Capacity Collaborative (Cooperative Agreement #AID-OAA-A-12-00058) and expanded under Breakthrough ACTION (Cooperative Agreement #AID-OAA-A-17-00017) both under the leadership of Johns Hopkins Center for Communication Programs. This website is now maintained by Johns Hopkins Center for Communication Programs and its contents are the sole responsibility of CCP. The contents of this website do not necessarily reflect the views of USAID, the United States Government, or Johns Hopkins University.
